LED Light Bulb Conversion Chart
Posted by LampsOne Admin on 13th Jun 2018

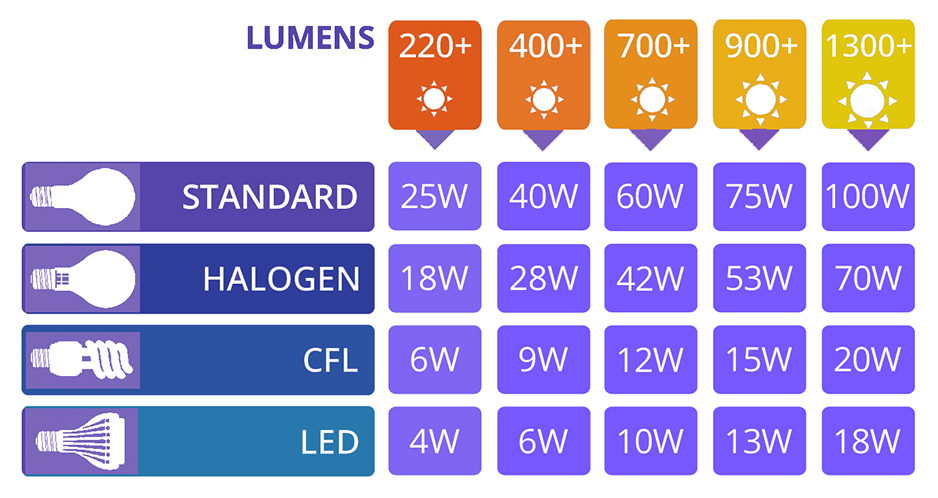
Lumens and Wattage
Light bulbs bring objects to life, different lighting temperatures set the mood, they make it safer to walk across spaces and can even decorate and highlight specific locations. There are three main categories of electric lights, each with its advantage and disadvantage. They are incandescent lamps, gas-discharge lamps (such as fluorescent bulbs) and LED lamps.
LED lamps were the most recent lights to be introduced and since then a new method of rating was required since the wattage no longer determined which bulb had the superior brightness.
The Different Types of Light Bulbs
In the past wattage determined how bright a light bulb would be, were more wattage meant more brightness. Now, LED’s have changed the game as an LED bulb the uses 15-Watts is no way similar to a 15-Watts Incandescent. Nowadays, companies rate bulbs through lumens as these give you a more accurate indication of how much light to expect from an LED.
| Metal Halide / High Pressure Sodium to LED Wattages Conversion | ||
| Original Lamp | LED Lamp | |
| 70 Watt Metal Halide | 30 Watt LED | |
| 100 Watt Metal Halide | 40-50 Watt LED | |
| 150 Watt Metal Halide | 60-70 Watt LED | |
| 175 Watt Metal Halide | 80-90 Watt LED | |
| 70 Watt High Pressure Sodium | 40 Watt LED | |
| 100 Watt High Pressure Sodium | 50-60 Watt LED | |
| 150 Watt High Pressure Sodium | 80-90 Watt LED | |
| 250 Watt High Pressure Sodium | 90-125 Watt LED | |
The LED lights trend
In recent years LED’s have been the norm for people as they have many advantages. Watts do not measure brightness but the amount of power used. Since LED’s use lesser wattage and produce the same amount of brightness, they save much more energy. Other than helping lower the electric bills; most LED bulbs are also dimmable and don’t contain any Mercury.
Choose the Right Bulb
Check the conversion chart to figure out the best bulb you need to replace old ones.

